
Curing advanced ovarian cancer; now on the horizon
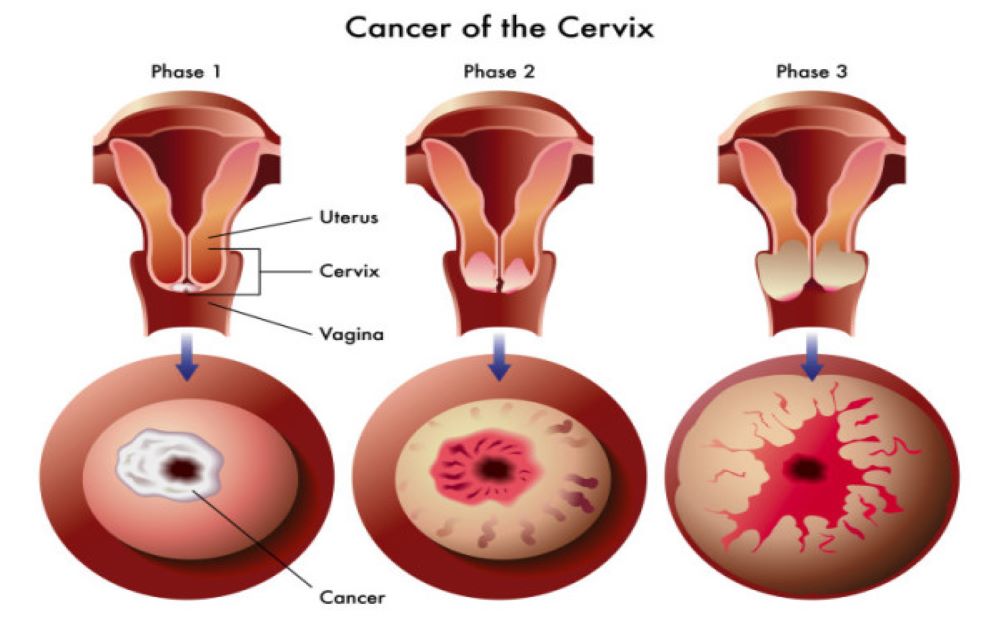
Approximately 75,000 women were diagnosed with cervical cancer in 2020. Unfortunately, due to lack of awareness regarding this disease, the majority (60%) are diagnosed in advanced stages and many succumb to this illness. Cervix is the lower portion of the uterus which connects it to the vagina. Cancer of the cervix is the 2nd most common malignancy diagnosed in Indian women.
Here are some of the most important questions frequently asked about cervical cancer
- Is there a way to prevent cervical cancer from occuring ? YES. Cervical cancer is one of the few cancers in humans which can be prevented. It is now known that cervical cancer occurs because of a virus (Human Papilloma Virus- HPV). This virus causes mutations in the normal cells lining the inner cervix which gradually transforms into cancerous cells. There are vaccines available for cervical cancer which provide immunity against this virus (eg. Gardasil-9). It should be given to all girls and unmarried women between the ages of 9-26 years. It reduces the risk of developing cervical cancers by 100% !
- Are there any other ways to reduce the risk of developing cervical cancer ? YES. High risk sexual behaviour (having unprotected sex with multiple sexual partners) increases the risk of getting infected with the HPV. Safe sex should be practiced, such as using a condom every time during sex. Getting infected with other sexually transmitted infections also increases the risk of HPV infection. Smoking also increases this risk.
- Are there any tests by which cervical cancer can be detected early by screening ? YES. A simple pap smear (a painless test, swab taken from the cervix with a spatula) is the most effective way to detect cervical cancer at a very early stage. ALL women should start screening for cervical cancers once they cross the age of 21. Pap smears should be done every 3 years till the age of 65 (this applies to women who have undergone surgical removal of the uterus as well).
- What are the symptoms one can develop if they have cervical cancer ? The most common symptoms are abnormal vaginal bleeding, usually after sexual intercourse. This may be associated with clear or foul smelling vaginal discharge. If the disease advances, it can cause lower back pain, difficulty in passing stools/urine as well.
- What is the treatment success rate for cervical cancer ? This depends mostly on the stage in which the cancer is diagnosed. For stage I disease which is treated with local surgical procedures, the cure rate is more than 95%. For stage II disease , the cure rate drops slightly to 80-90%. For larger stage II and stage III tumors that are treated with chemo-radiation, the cure rate drops further to 70-80%. For stage IV cancers, neither surgery nor chemo-radiation are possible. Only chemotherapy is given which does not cure the patient, but can prolong the patients survival to an average of 1.5-2 years. As you can see, the best chance of curing the patient is when it is diagnosed at an early stage !
Please raise awareness about this preventable cancer.
Get your sisters/daughters vaccinated against Human papilloma virus (HPV)
Encourage the women in your family to get regular PAP smears.